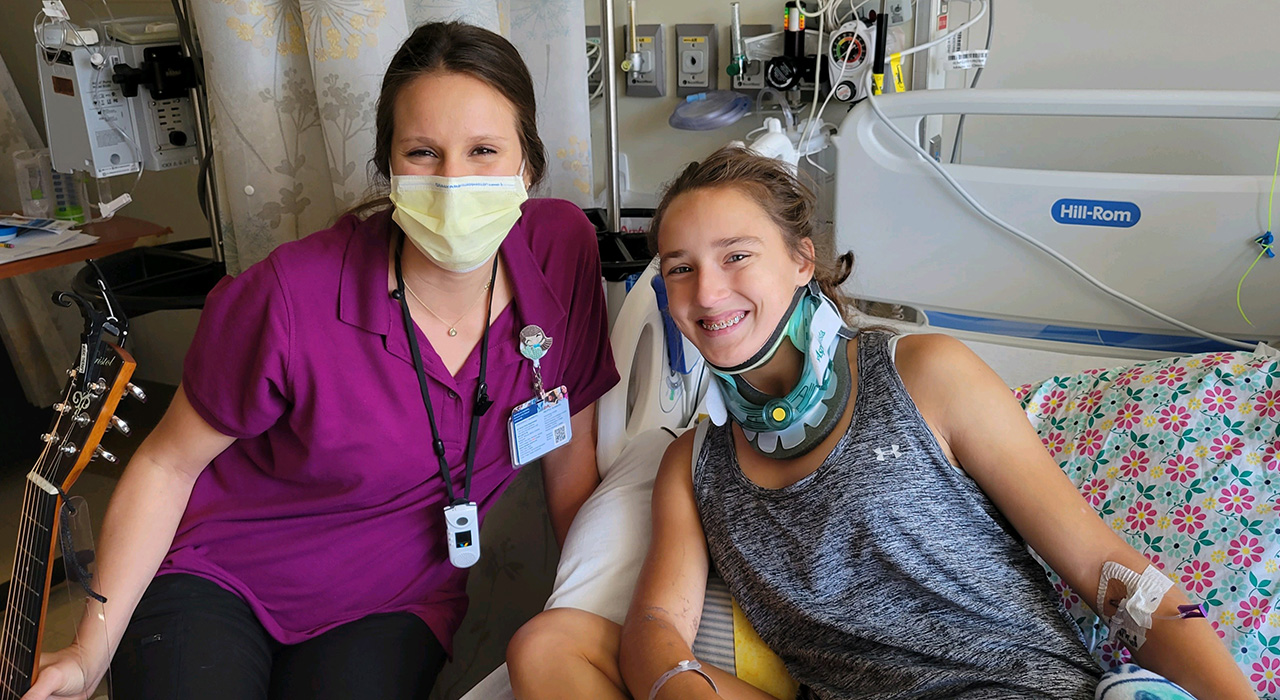
Fewer hospital-to-hospital transfers with telemedicine
New UC Davis Health research confirms that pediatric critical care telemedicine consults with clinicians in rural and community emergency departments result in significantly fewer interfacility transfers. Authors said the study, published in JAMA Network Open, is the first randomized clinical trial assessing the impact of telemedicine consults on transfer rates compared to the current standard of care, telephone consultations.
Over two decades of PECARN power
The Department of Emergency Medicine renewed its four-year, $2.8 million grant with the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN). The network and its major studies have helped care teams across the U.S. make treatment decisions with more evidence-based confidence — and less side effects on children. The group of 18 pediatric emergency departments in academic, urban and rural hospitals serves more than 1 million acutely ill and injured children every year. Nathan Kuppermann, M.D., Bo Tomas Brofeldt Endowed Chair of Emergency Medicine was one of its founding principal investigators in 2001.
Emergency department preparedness cuts mortality risk in children
A six-year study, co-authored by Nathan Kuppermann, M.D., showed that emergency departments with high pediatric readiness standards have lower pediatric mortality rates. Involving nearly 800,000 children receiving emergency care in 11 states, investigators found that injured children had a 60% reduced chance of in-hospital death, and those with acute medical conditions had a 76% reduction. Authors of the study believe these results have national policy implications.
Working to predict mental health issues after concussions
Researchers at UC Davis Health and the Kennedy Krieger Institute have received a five-year, $2.5 million grant from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to study adolescent mental health following a concussion or traumatic brain injury. The health care teams will develop and validate a prognostic tool in hopes to provide evidence for clinical decision-making, help reduce uncertainty amongst clinicians, and decrease health disparities for patients.