Resident Program - Case of the Month
March 2021 – Presented by Dr. Jiejun Wu (Mentored by Dr. John Paul Graff)
Discussion:
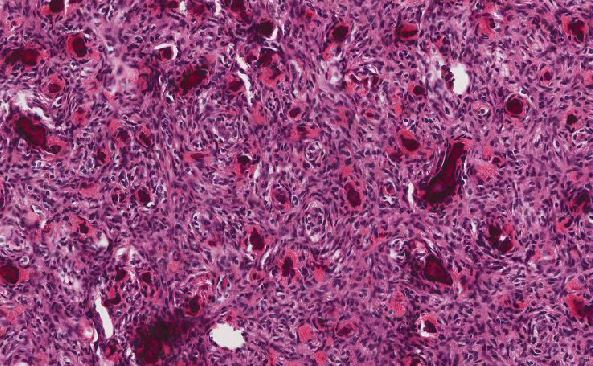
Fungal lymphadenitis is rare in the immunocompetent population and it is often found in immunocompromised patients because of HIV, malignancy, or other immunosuppressive diseases. The most common fungi causing lymphadenitis in immunocompromised patients include H. capsulatum and C. neoformans. The lymph nodes infected with H. capsulatum show granulomatous inflammation though the granuloma may be poorly formed or absent in these immunocompromised patients. This HIV patient has a recent history of histoplasmosis, his microscopic findings are consistent with fungal lymphadenitis which is confirmed by GMS-F and PAS staining. Further correlation with microbiologic study may be needed for final diagnosis.
Fungal lymphadenitis needs to be differentiated from lymphadenitis caused by HIV itself. Correlating with disease advancing, HIV lymphadenitis shows progressing histologic patterns from reactive follicular hyperplasia to atrophic lymph node featured with burnt-out follicles and extensive vascular proliferation. Another group of differential diagnosis are lymphomas associated with HIV infection. HIV-associated lymphomas include those also occurring in immunocompetent patients, such as Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cells lymphoma (DLBCL), plasmablastic lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, etc. Other lymphomas, including primary effusion lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma, and HHV8-positive DLBCL, NOS, are more specifically found in HIV patients. The third group of HIV-associated lymphomas that occur in both HIV and other immunocompromised states show polymorphic lymphoid proliferations resembling post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. It should be noted that association with EBV infection is one feature of HIV-associated lymphomas though this association varies with the site of lymphoma presentation and histologic subtypes. In this patient, extensive immunostaining tests, which turned out to be negative for lymphoma, were performed to rule out lymphoma and therefore, the correct answer is "Fungal lymphadenitis caused by histoplasmosis" based on these testing results and morphological evaluation.
References:
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th, 2017
- Hematopathology: A Volume in the High Yield Pathology Series, 1st, 2013
- Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 2nd, 2018

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director