February 2024 – Presented by Dr. Yuden Pemba (Mentored by Dr. Karen Matsukuma)
A 27-year-old woman from Afghanistan with no significant past medical history presented with intermittent abdominal pain. The pain localized to the right upper quadrant with occasional radiation to the left upper quadrant and right flank. On abdominal ultrasound, large cysts in both the liver and spleen were identified. Subsequent serologic testing revealed elevated antibody titers for an infectious agent, and she was treated with albendazole twice daily for 2 months. Two years later, a repeat blood test and ultrasound showed a complex hypoechoic lesion measuring 9.2 x 8.8 cm in the right lobe of the liver and a smaller lesion (2.4 x 2.2 cm) in the spleen. She was prescribed albendazole again for 3 months. At one year, an MRI showed multiple cysts within the liver, the largest of which measured 10 cm and was located in the right lobe. Additionally, at least one cyst was identified in the spleen, measuring up to 2.3 cm. Due to the increase in size of the cysts, the patient underwent surgical resection.
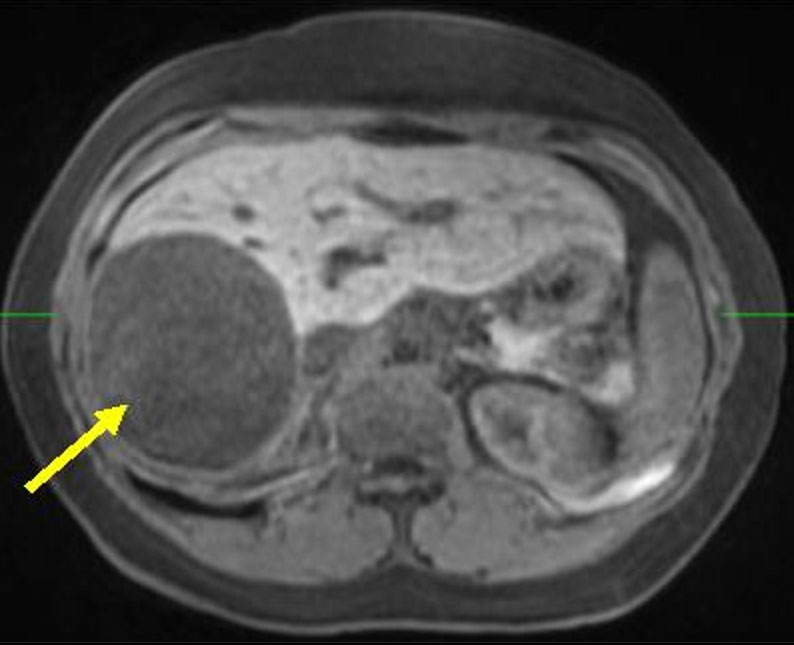
Figure 1: MRI shows the large liver cyst (yellow arrow).
Gross Examination
The liver specimen consisted of a 223.6 gm, 15.0 x 13.1 x 5.5 cm aggregate of tan-yellow, rubbery curvilinear tissue with adherent yellow grumous debris and a red-tan 9.1 x 4.5 x 3.9 cm candidate cyst wall with adherent yellow grumous material on one side and a smooth surface on the opposite side. The thickness of the candidate cyst wall ranged from 0.2 to 0.4 cm.
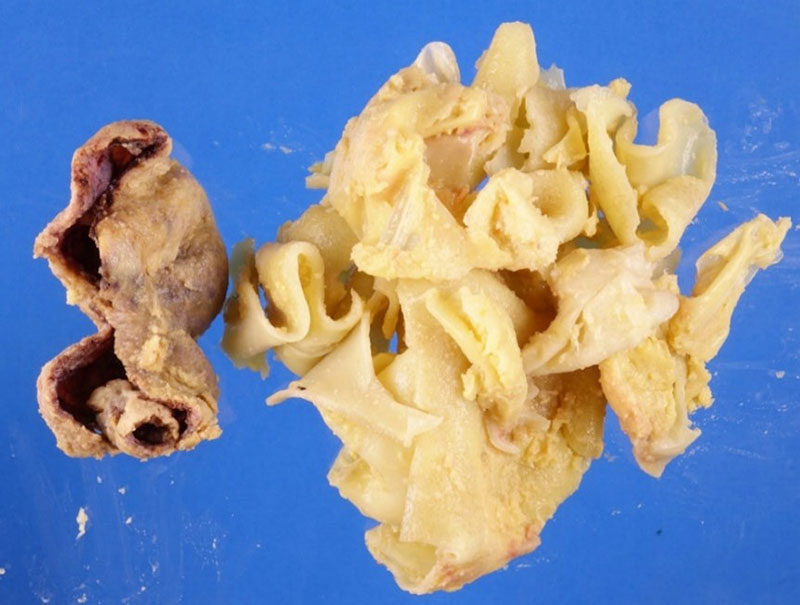
Figure 2. Liver specimen.
The separately submitted spleen (247.8 gram, 10.8 x 8.3 x 6.3 cm) demonstrated a well-circumscribed a 4.0 x 2.1 x 1.6 cm thin-walled cyst filled with tan-yellow, rubbery curvilinear tissue, similar to that of the liver specimen.
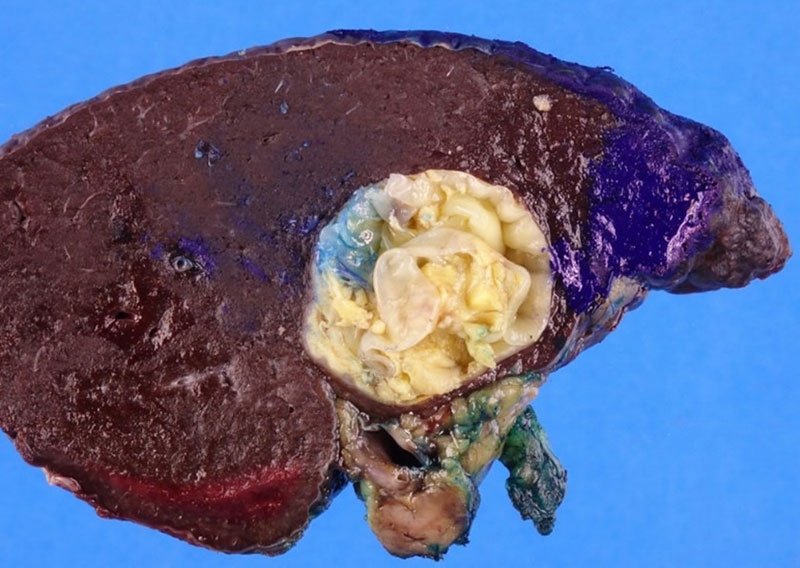
Figure 3. Splenic cyst.
Histopathologic Sections
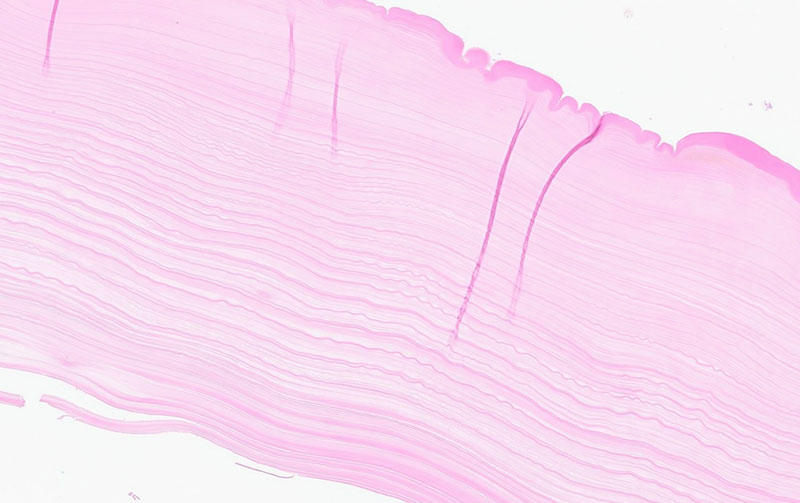
Figure 4. Acellular laminated layer corresponding to the tan-yellow rubbery tissue found in the liver cyst.
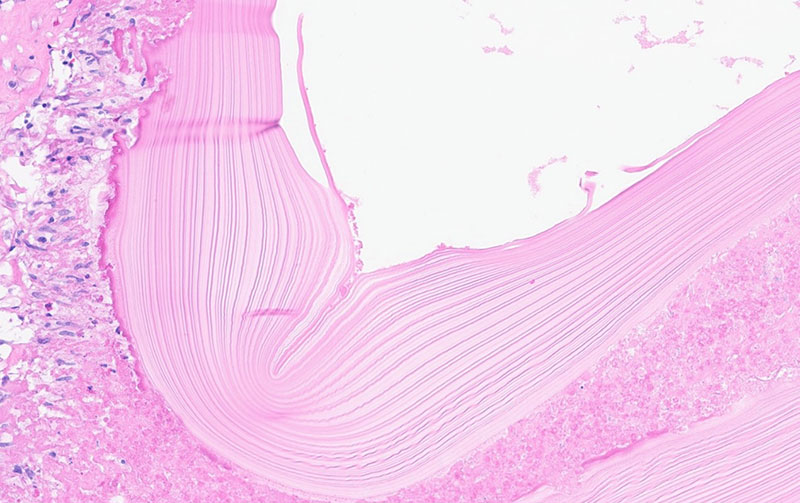
Figure 5. The same acellular laminated eosinophilic layer is present in the splenic cyst.
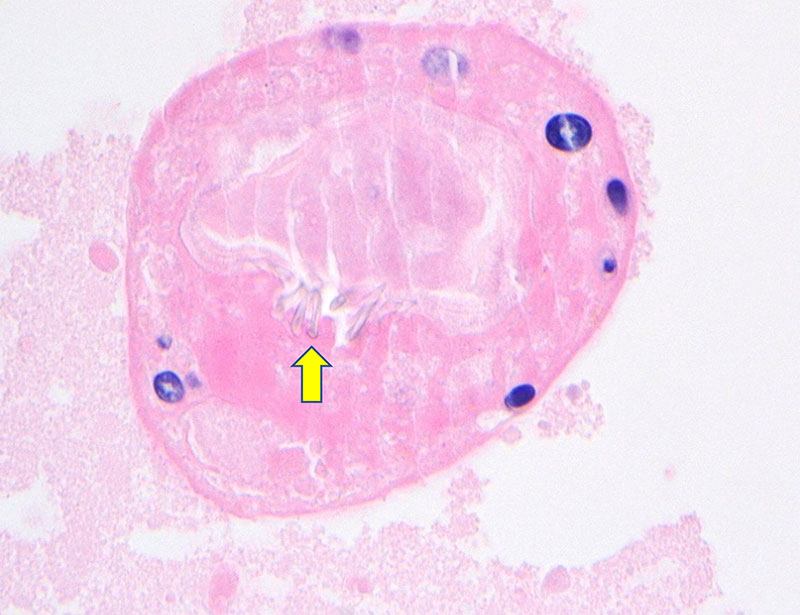
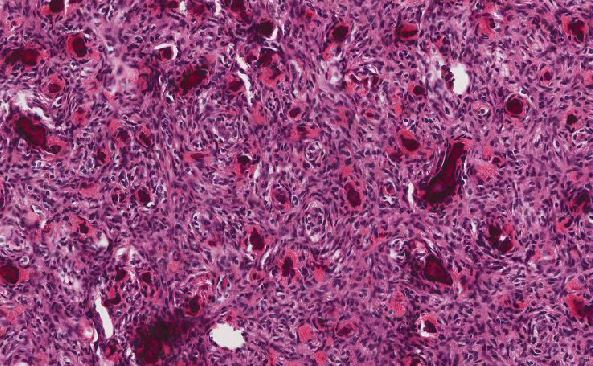
Figure 6. A partially calcified scolex within the debris of the liver cyst with refractile hooklets (yellow arrow)
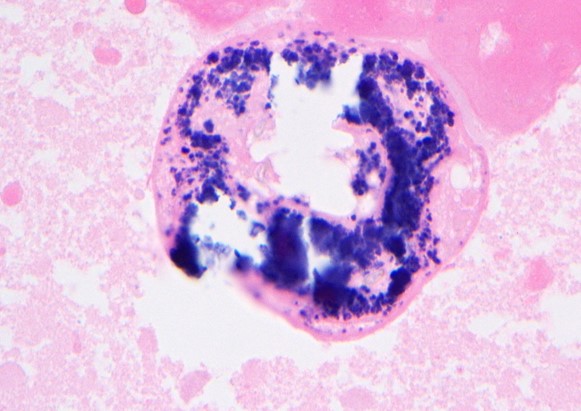
Figure 7. Additional calcified scolex found within the debris of the liver cyst.

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director