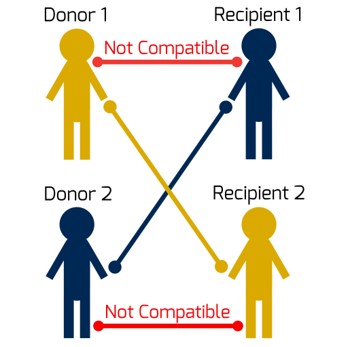
Paired Exchange
The first tests done for all donor-recipient pairs are blood type testing and a crossmatch test. These tests determine whether the donor and recipient are compatible. In the past, if a pair was not compatible, the recipient had no other option and remained on the waiting list for a kidney from a deceased donor.