Warfarin
What is Warfarin?
Warfarin (also known as Coumadin) is an anticoagulant that prevents new blood clots from forming and existing ones from growing larger. It is often referred to as “blood thinner.”
Some conditions that warfarin can be used for include:
- Atrial fibrillation/stroke prevention
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT or blood clot in vein)
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lung)
- Heart valve replacement
- Hypercoagulability
- Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD)
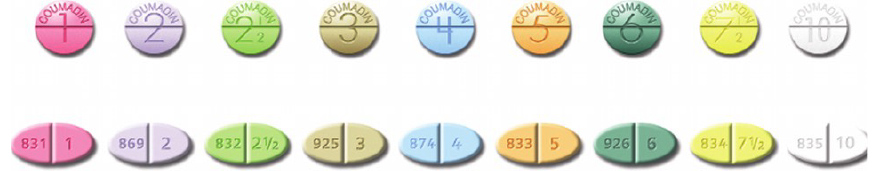
Warfarin Tablet Colors
Each warfarin tablet color represents a different strength. Regardless of the manufacturer of your warfarin, the color will remain the same for each tablet strength.
INR Monitoring
Warfarin is monitored with a blood test, called the International Normalized Ratio (INR) to determine how well warfarin works. The INR helps healthcare providers determine whether the dose needs to be adjusted to balance both the risk of clotting and bleeding. At the beginning of warfarin therapy, the INR will be checked more frequently, about 1-2 times weekly. Once a stable dose has been established, the INR checks will be less frequent.
If you have trouble going to the lab, you may have the option of using a home machine to monitor your INR. Please contact our clinic for more information if you are interested.
Diet Interactions
Warfarin interacts with Vitamin K, which can be found in certain foods, such as dark green leafy vegetables. It is not necessary to eliminate these foods from your diet but instead to keep your diet as consistent as possible. Please contact our clinic for a more detailed list of foods containing high Vitamin K content.
Medication/Dietary Supplements Interactions
Notify your doctor and the Anticoagulation Clinic about any changes in your medications, including over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some of your other medications may increase the risk of bleeding while on warfarin. They can also directly affect the way warfarin works and increase or decrease the INR.
Procedures
Warfarin may need to be stopped briefly before certain procedures. Tell all your providers, including dentists, that you are taking warfarin. Notify the Anticoagulation Clinic about any upcoming procedures and if your surgeon or dentist has specific instructions on when to stop warfarin prior to a procedure.
New Patient Welcome Packet
If you are a recent patient to the Anticoagulation Clinic, please download, fill the form out and mail or fax it to our clinic.
Warfarin
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that prevents new blood clots from forming and existing ones from growing larger.
Learn more about Warfarin
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOAC)
Directly acting oral anticoagulants (DOAC) include a direct thrombin inhibitor (dabigatran) and factor Xa inhibitors (rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban).
Learn more about Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOAC)
Injectable Anticoagulants
Outside the hospital, injectable anticoagulants may be used as a “bridge” for when you are starting warfarin or stopping warfarin for a short period of time.
Learn more about Injectable Anticoagulants
