Residency Program - Case of the Month
July 2015 - Presented by Dr. Saba Ali
History:
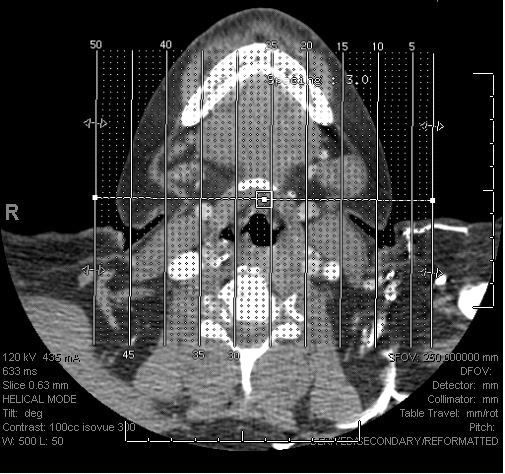
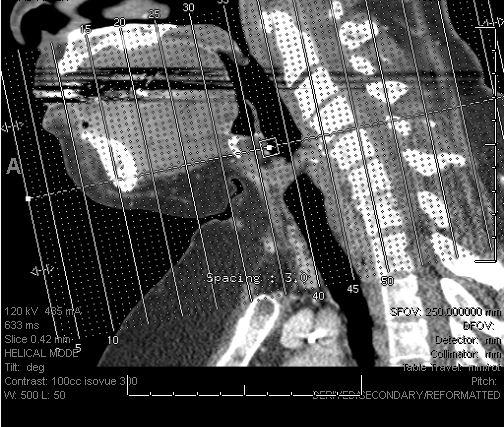
The patient is a 64-year-old female with an unremarkable past medical history who presented for evaluation of a slow growing swelling on the floor of her mouth. Physical examination revealed a firm mass (2.7 x 1.1 cm) that appeared confined to the right side with normal overlying mucosa. A CT soft tissue scan of the neck with contrast revealed a 2.1 x 1.4 x 1.6 cm mass (Figures 1 and 2) on the right anterior floor of mouth which extended anteriorly across the midline by 5 mm, without definite invasion of the mylohyoid or right mandible, and with possible invasion of the right sublingual salivary gland. Small bilateral lymph nodes in levels 1 and 2 were identified without necrotic adenopathy.
|
Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
 |
 |
A subsequent biopsy of the mass was consistent with carcinoma. The patient was taken to surgery for an anterior floor of mouth resection with bilateral neck dissection and radial forearm free-flap reconstruction. Intraoperative frozen section analysis of the margins of the right posterior floor of mouth, proximal lingual nerve, and level 2 lymph nodes were negative for carcinoma. Permanent histopathology revealed a single, bilateral tumor focus with no evidence of perineural or lymphovascular invasion, and of 28 lymph nodes examined, 0 were involved. The tumor was well-encapsulated and present 1 mm away from the nearest surgical (superior) margin. Pathologic staging was T2N0M0. The patient was doing well without recurrence one month after follow-up with only mild dysarthria.
Gross
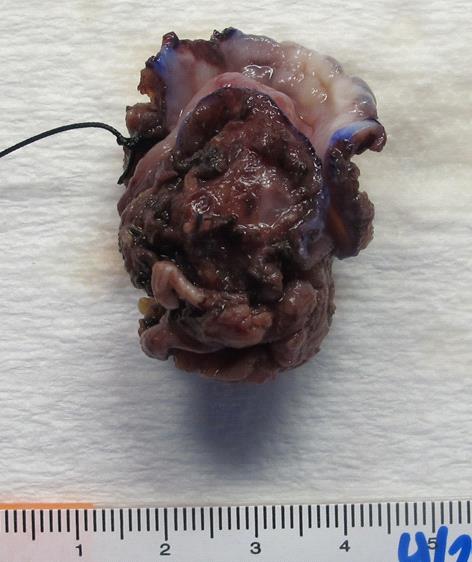
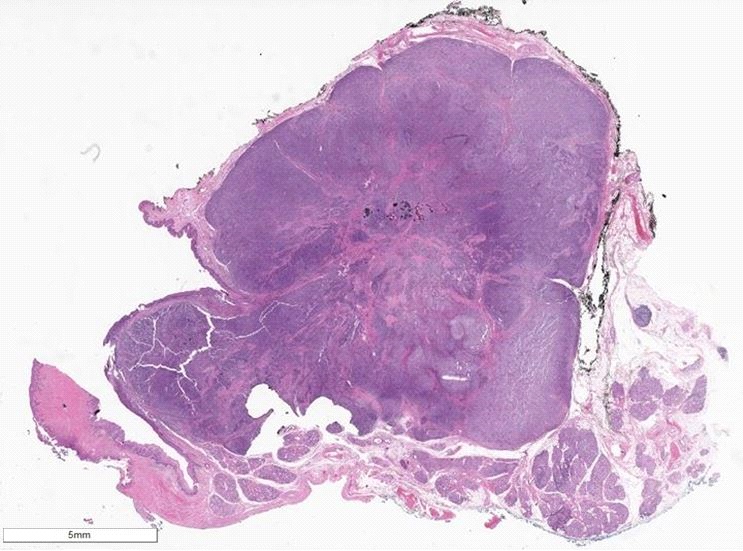
Received in formalin, labeled with the patient's name and unit number, and undesignated, is an oriented 4.6 x 3.0 x 1.8 cm specimen with a suture designating the left side. The specimen consists of mucosa anteriorly (4.0 x 1.1 x 0.3 cm) and posteriorly attached irregular and roughened circular soft tissue (3.2 x 1.8 x 1.5 cm). The inferior surface is inked blue, and the soft tissue superior surface is inked black. Externally on the mucosal surface is a polypoid mass (1.1 x 0.6 x 0.4 cm) covered with mucosa present 0.6 cm from the anterior mucosal margin, 0.8 cm from the left mucosal margin, and 0.8 cm from the right mucosal margin. Cut sectioning reveals a well circumscribed tan white firm lesion (2.2 x 1.2 x 0.8 cm) without necrosis that abuts the superior margin and comes to within 1 mm of the inferior margin, and is present 0.6 cm from the anterior margin. There is a satellite nodule present (0.3 cm) covered with mucosa 0.4 cm from the right mucosal margin. The specimen is totally submitted.
|
Figure 3 |
 |
Microscopic Images
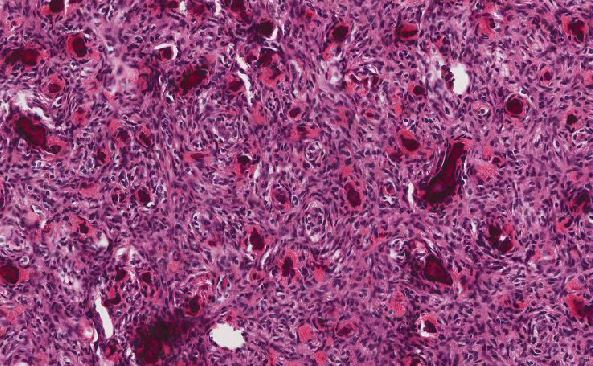
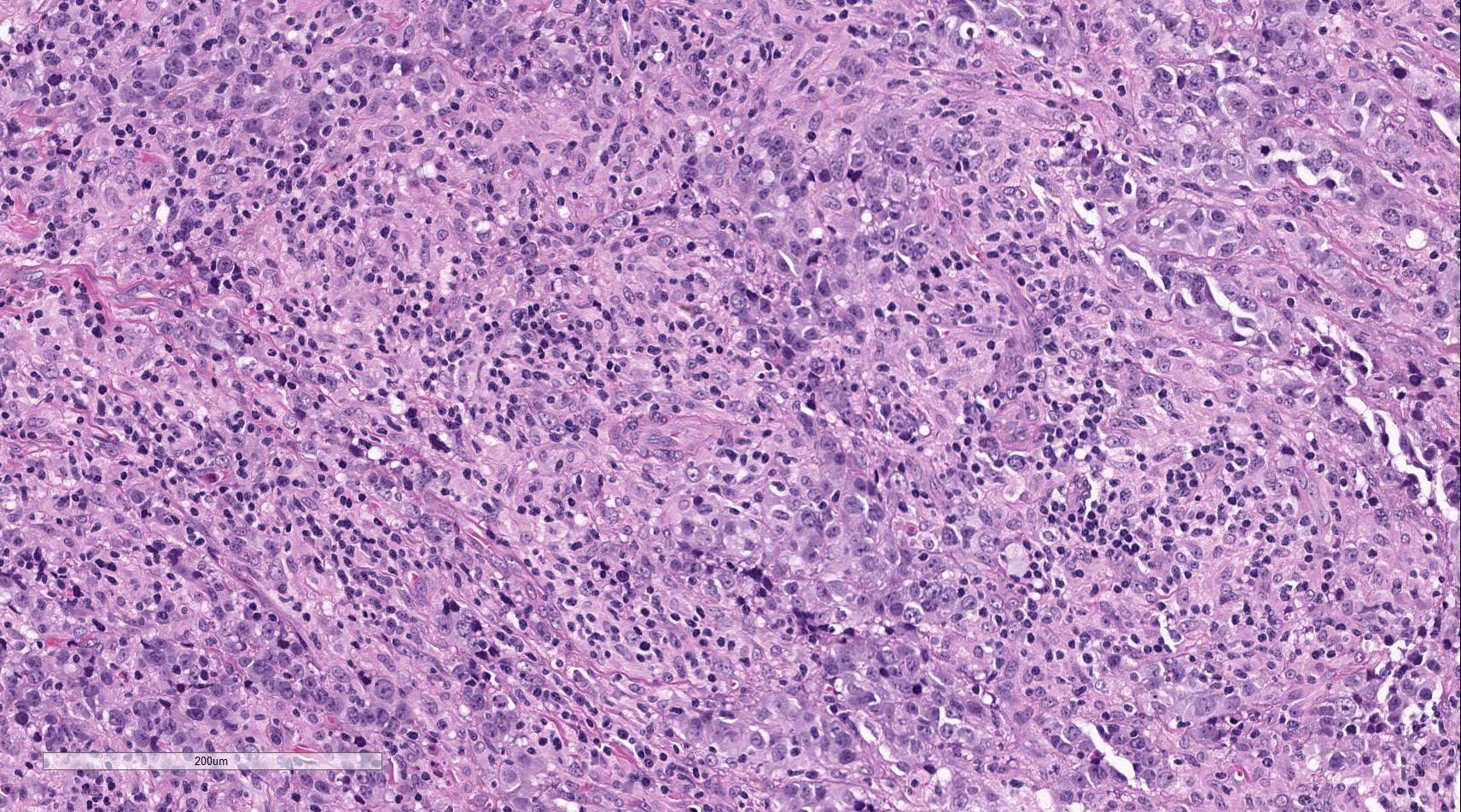
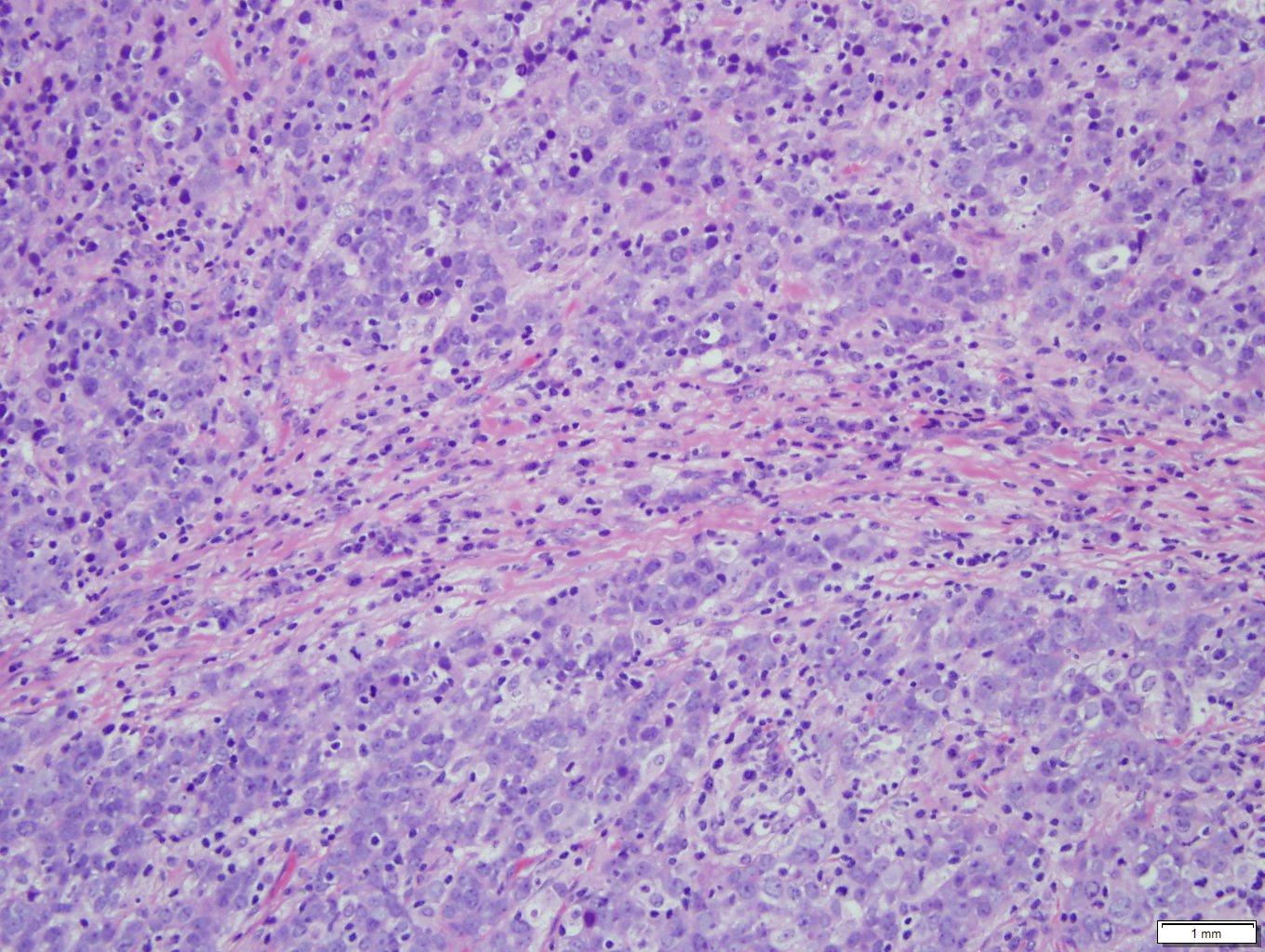
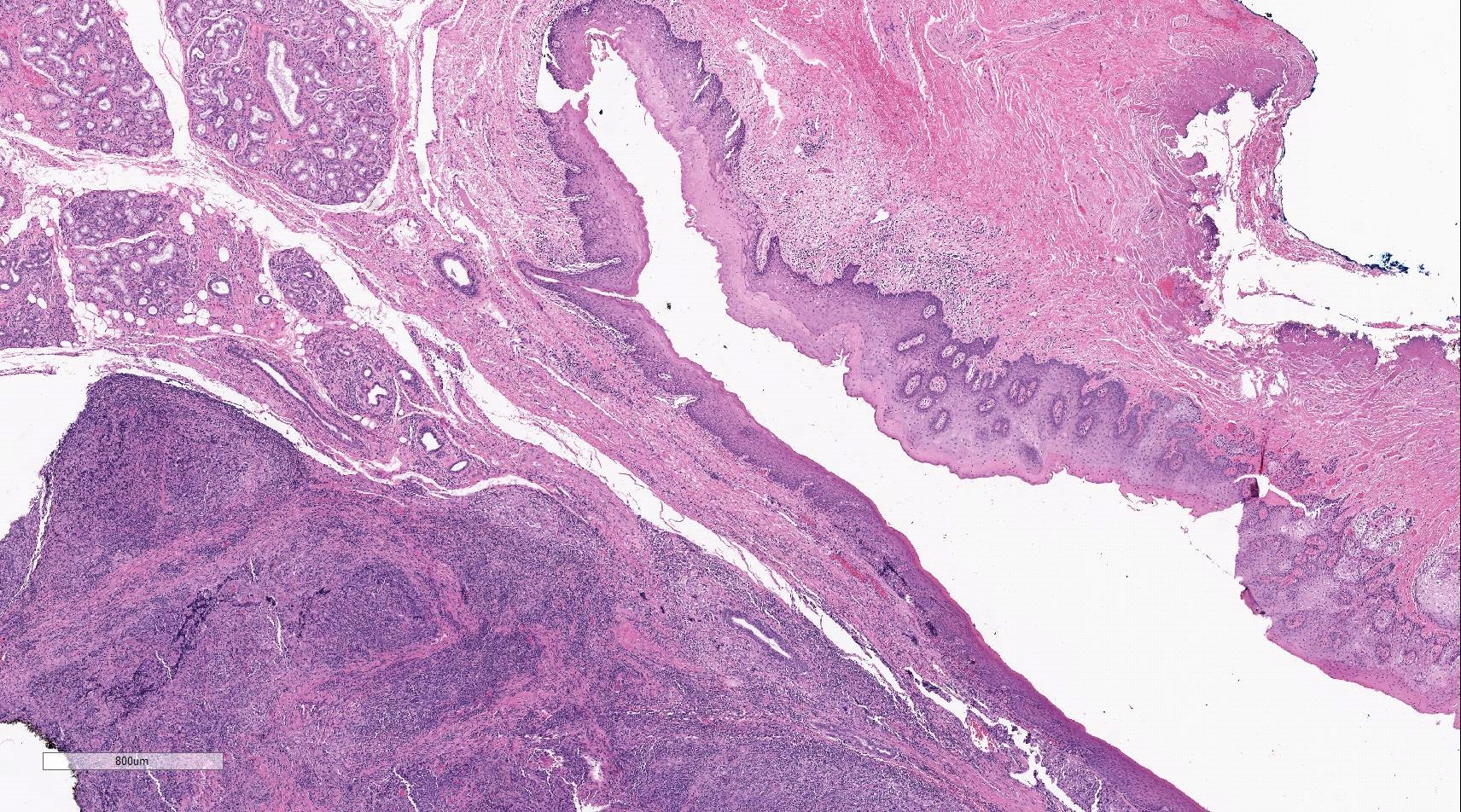
Histologically, the tumor was composed of a poorly lobulated architecture with an intact overlying squamous mucosa and capsule (Figures 4 and 5), composed of cohesive sheets of an atypical monotonous population of infiltrating epithelial-like cells without surrounding desmoplasia. The tumor cells had vesicular nuclei with prominent nucleoli, mild to moderate lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm with ill-defined cell borders. Dispersed in the background were numerous lymphocytes and plasma cells (Figures 6 and 7). Abundant mitotic figures, keratinization, and necrosis were not identified.
|
Figure 4 |
|
Figure 5 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
| Figure 6 | Figure 7 | |
 |
 |
Immunohistochemistry
EBER-ISH: Negative
Answer

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director