Experimental gene therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration offers promise for older adults
Wet age-related macular degeneration, or AMD, affects approximately 2 million people in the United States, Europe and Japan. It is a leading cause of vision loss among older adults. A new gene therapy being tested at UC Davis Health may offer a better treatment option.
“Vision loss can have a major impact on the quality of life for older adults. Difficulties an older adult might experience are a loss of independence and no longer being able to drive or go places without assistance. This increases the risk of social isolation and loneliness,” said Rebecca Boxer, chief of the UC Davis Health Division of Geriatrics, Hospice and Palliative Medicine. “Additionally, loss of vision increases the risk of falls and injury.”
Ophthalmologists at UC Davis Health used an experimental gene therapy last summer to treat a patient with wet AMD. It was the first time the UC Davis Eye Center had used gene therapy.
“The current treatments for wet AMD may be life-long, and injections can be as frequent as every month,” said Glenn Yiu, professor of ophthalmology at UC Davis Health and principal investigator for the new clinical trial. “If approved, a gene therapy solution has the potential to maintain vision while reducing the number of injections by allowing the eye to continuously produce the medicine on its own,” Yiu said.
The treatment was part of a randomized, partially masked, controlled, phase 3 clinical study evaluating the efficacy and safety of an experimental therapy, ABBV-RGX-314, for wet AMD. UC Davis Health is one of 93 sites in the U.S. participating in the clinical trial. This investigational treatment is not FDA approved, and the efficacy and safety have not been established.
In AMD, the macula, an area of the eye’s lining that helps you see, becomes damaged. This can blur the central part of your vision, making it hard to drive or read. An early symptom of wet AMD is that straight lines look distorted and wavy.
In wet, or neovascular AMD, abnormal blood vessels grow underneath the retina. These vessels lead to bleeding or fluid leakage in the back of your eye, causing vision loss. This process, known as “neovascularization,” is largely driven by a growth factor called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
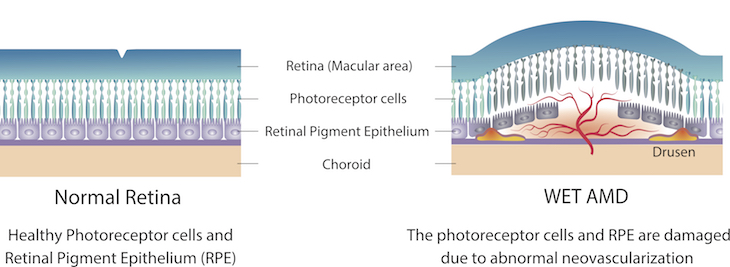
Treatments for wet AMD rely on repeated injections of drugs that block VEGF in the diseased eye.
Gene therapy may offer different approach
Unlike stem cell therapies used to treat eye diseases — which involve injecting cells with regenerative or restorative capabilities into the eye — gene therapy generally uses an empty viral envelope (a vector) to deliver a gene with specific genetic instructions for making protein.
ABBV-RGX-314 contains genetic instructions for making anti-VEGF proteins. After a single injection of ABBV-RGX-314 gene therapy, the eye can start to make the medicine on its own.
Yiu performed the first experimental gene therapy eye surgery at UC Davis Health in July. The procedure is more complex than administering a monthly injection. It includes a vitrectomy, where the viscous gel in the eye is removed and replaced with a saline infusion. The experimental treatment with its gene delivery vector is then injected underneath the retina.
Yiu will monitor whether the participant will continue to need monthly anti-VEGF injections in the coming months.
“Gene therapy for wet macular degeneration is potentially an exciting new therapy since it may reduce the burden of treatment, which presently requires regular visits to the ophthalmologist for frequent injections,” Boxer said.
UC Davis Health has enrolled three patients in the clinical trial and plans to enroll more. Individuals aged 50 to 88 with wet AMD who have had prior anti-VEGF injections may be eligible to participate.