Intellectual Developmental Disabilities
IDDRC Rodent Behavior Core

The UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC Rodent Behavior Core (RBC) supports multidisciplinary research focused on mouse and rat models of autism and other neurodevelopmental disabilities, including Angelman syndrome, Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, and Rett syndrome. Our overarching goal is to advance the diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and amelioration of intellectual and developmental disabilities. RBC Projects include mechanistic and translational investigations designed to discover clinically effective therapeutics. Innovative rodent behavioral tests, many developed by the RBC director and co-directors, parallel clinical tests developed and used by clinical investigators through the IDDRC Clinical Translational Core (CTCx). The internationally recognized scientific excellence and cutting-edge expertise of RBC leadership, combined with ongoing interactions of the RBC and other IDDRC rodent cores around the U.S., contribute to the national leadership role of the RBC in the standardization of rodent behavioral testing methods to promote rigor and reproducibility.
The Rodent Behavior Core offers four tiers of services:
Tier 1: Consultation on hypothesis-driven choices of behavioral assays, experimental design, generation of IACUC protocols, interpretation of findings, preparation of results for publication, preparation of preliminary data and methodological text for grant proposals. The RBC is committed to ensuring that the animal models being used clearly address the scientific questions proposed for investigation.
Tier 2: Access for IDDRC investigators to state-of-the-art behavioral testing equipment and facilities.
Tier 3: Training and supervision of IDDRC investigators and their postdoctoral fellows, graduate students, undergraduates, and technicians in mouse and rat behavioral testing protocols, use of behavioral testing equipment, drug administration for translational behavioral pharmacology studies, and tissue harvesting.
Tier 4: Conducting all aspects of an IDDRC study by the RBC staff, including behavioral testing, breeding colony management, special diets, drug treatments, and tissue harvesting.
The RBC further offers:
• Development of reliable new assays requested by users
• Access to a broad range of mutant mouse and rat models
• Facilities for harvesting tissue from behaviorally tested mice and rats
• Metabolic monitoring equipment and expertise
• Electroencephalograpy equipment and expertise (awake telemetry EEG)
• Guidance about resources at UC Davis, including a formal agreement with the UC Davis Mouse Biology Program, which includes subsidies to support generation of new mutant rodents using advanced CRISPR technologies for projects that will use the RBC (see Administrative Core for details).
• Facilitation of collaborations between IDDRC investigators at UC Davis and nationally
IDDRC investigators initially contact one of the core leaders to discuss new projects. Formal initiation to request IDDRC approval for services is completed through the IDDRC REDCap system. Full descriptions and illustrations of the mouse and rat assays offered by the RBC are displayed on the UC Davis IDDRC website. IDDRC-approved projects are typically scheduled on a first-come, first-served basis. Consultation meetings between RBC leadership and staff and IDDRC investigators contribute to quality control. RBC members conduct or advise on proper statistical analyses and acceptable graphical presentation of the data in conjunction with the Biostatistics, Bioinformatics, and Research Design Core. Necessary control assays are recommended. Potential artifacts detected by the control assays are discussed with the IDDRC investigator, and advice is provided on accurate interpretations of results from hypothesis-driven behavioral assays.
Acoustic Startle
Threshold for hearing and startle response is assayed in the San Diego Instruments automated SR-Lab apparatus. Tones from 80 to 120 decibels are randomly presented. Amplitude of whole body flinch is measured by a stabilimeter.
Developmental milestones
Physical and behavioral measures of early development are scored at postnatal days 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14. Physical parameters include body weight, body length, tail length, fur development, eye opening, pinna ear detachment and incisor tooth eruption. Behavioral parameters include righting reflex, negative geotaxis, cliff aversion, forepaw grasping reflex, Preyer startle, level screen, screen climbing, and bar holding.
DigiGAIT
DigiGAIT allows for automated investigation of temporal and spatial gait parameters of mice and rats from neonatal development through aging and gait decline. The DigiGAIT treadmill system collects numerous parameters such as wide or narrow stances, increased and reduced stride length, stride frequency, and altered stride dynamics, The DigiGAIT does not rely on context novelty so there is no effect of test-retest, making it an ideal outcome for within subject therapeutic testing.
Drug treatments (by special request only)
Acute and chronic administration of compounds, using intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, oral, and intranasal routes of administration, can be conducted by investigators in the dedicated procedure room, or can be conducted by Core staff upon request.
EEG

Electroencephalograpy using telemetry to detect seizures, sleep architecture, and power spectral analyses. Spiking events and powerband calculations are collected via wireless telemetry and automatically scored using Neuroscore. Custom algorithms tailored to investigator questions are also offered upon request, such as active-wake-sleep cycles and circadian rhythms.
Elevated plus-maze

Anxiety-related behavior is assayed in a Med Associates photocell-equipped automated elevated plus-maze. The innate conflict is between the tendency of mice and rats to explore a novel environment versus their preference to avoid the two brightly lit open raised arms by staying in the two dark enclosed arms. Percent time in the open arms and number of open arm entries are increased by anxiolytic treatments. Total number of entries provides the built-in control for general exploration, sedation and hyperactivity confounds.
Fear Conditioning

Contextual and cued fear conditioned learning and memory are assayed in the automated Med Associates Fear Conditioning Chambers apparatus equipped with near infared cameras and Video Freeze Software. Pairing of aversive mild footshock with chamber context cues and an auditory cue is conducted on training day 1. Contextual conditioning, defined by episodes of freezing in the identical environment, is scored on day 2. Cued conditioning, defined by episodes of freezing to the auditory cue in a different environment, is scored on day 3.
Footprint gait
Ataxic gait is assayed by observation of footprint path. Forepaws and hindpaws are painted with nontoxic Crayola paint colors. The mouse or rat walks rapidly across white paper, moving from a brightly lit area to a dimly lit area. Colored footprints on the paper are subsequently measured by the investigator to quantify forepaw width, hindpaw width, stride length, and deviations from the straight line mean of the footprint path.
Forced Swim
 The Porsolt forced swim test for antidepressant response is assayed in an inescapable transparent Plexiglas cylinder filled with 25 °C tap water. Rats and mice will swim at first, then display episodes of floating immobility. Floating is scored during the last 4 minutes of a 6 minute test session, by a trained observer, from videos of the session.
The Porsolt forced swim test for antidepressant response is assayed in an inescapable transparent Plexiglas cylinder filled with 25 °C tap water. Rats and mice will swim at first, then display episodes of floating immobility. Floating is scored during the last 4 minutes of a 6 minute test session, by a trained observer, from videos of the session.
General health battery
Body weight, appearance of fur, eye blink, righting reflex, and other simple observational measures of general health are conducted in young or older mice.
Grip Strength
 The mouse is held with its forepaws grasping the triangular wire. Muscle strength is measured as latency to release forepaw hold of the wire bar, while the tail is gently pulled backward.
The mouse is held with its forepaws grasping the triangular wire. Muscle strength is measured as latency to release forepaw hold of the wire bar, while the tail is gently pulled backward.
Hot Plate
 The mouse is placed on a hot plate, heated to 55 °C. The plastic cylinder prevents the mouse from jumping off. Nociceptive response to the 55 °C thermal stimulus is measured by latency to first response, including licking a paw, jumping, or vocalizing. A 30 second cut-off avoids tissue damage.
The mouse is placed on a hot plate, heated to 55 °C. The plastic cylinder prevents the mouse from jumping off. Nociceptive response to the 55 °C thermal stimulus is measured by latency to first response, including licking a paw, jumping, or vocalizing. A 30 second cut-off avoids tissue damage.
Light-Dark Transitions
 The mouse is placed in the large, open, brightly lit side of a two chambered apparatus. The second chamber is small, enclosed, and dark. Photocells across the opening automatically detect movements of the mouse between compartments. The conflict is between the tendency of mice to explore a novel environment and the preference of mice to stay in a small, enclosed, dark environment. Anxiety-related parameters that are sensitive to treatment with benzodiazepines include number of transitions between compartments and time spent in the light compartment.
The mouse is placed in the large, open, brightly lit side of a two chambered apparatus. The second chamber is small, enclosed, and dark. Photocells across the opening automatically detect movements of the mouse between compartments. The conflict is between the tendency of mice to explore a novel environment and the preference of mice to stay in a small, enclosed, dark environment. Anxiety-related parameters that are sensitive to treatment with benzodiazepines include number of transitions between compartments and time spent in the light compartment.
Marble Burying
 Twenty black glass marbles are arranged in a symmetrical 4×5-cm grid on top of 2-3 cm deep bedding in clean, standard mouse cages with a filter top lid. Mice are given a 30-minute exploration period, after which the number of marbles buried is tallied by the investigator, as a measure of repetitive behavior.
Twenty black glass marbles are arranged in a symmetrical 4×5-cm grid on top of 2-3 cm deep bedding in clean, standard mouse cages with a filter top lid. Mice are given a 30-minute exploration period, after which the number of marbles buried is tallied by the investigator, as a measure of repetitive behavior.
Morris Water Maze
 The mouse is placed in a pool of 25 °C water, which is made opaque with non-toxic Crayola paint. A Plexiglas escape platform is located just under the surface of the water, invisible to the swimming mouse. On repeated training trials, the mouse learns the location of the hidden platform, based on environmental room cues. Acquisition is defined as reaching the hidden platform in 15 seconds or less. A probe trial is administered after acquisition, in which the platform is removed. Time spent in the previously trained quadrant, and number of crossings over the former location of the platform, confirm that the mouse learned the location of the escape platform using distal room cues. Reversal training is subsequently conducted by re-training with the platform in a different quadrant of the pool. Acquisition and reversal each require 4 to 8 days of training, conducted consistently by the same investigator.
The mouse is placed in a pool of 25 °C water, which is made opaque with non-toxic Crayola paint. A Plexiglas escape platform is located just under the surface of the water, invisible to the swimming mouse. On repeated training trials, the mouse learns the location of the hidden platform, based on environmental room cues. Acquisition is defined as reaching the hidden platform in 15 seconds or less. A probe trial is administered after acquisition, in which the platform is removed. Time spent in the previously trained quadrant, and number of crossings over the former location of the platform, confirm that the mouse learned the location of the escape platform using distal room cues. Reversal training is subsequently conducted by re-training with the platform in a different quadrant of the pool. Acquisition and reversal each require 4 to 8 days of training, conducted consistently by the same investigator.
Novel Object Recognition
 The subject mouse is placed in an open field containing two identical objects. At a time point such as one hour later, the subject is returned to the open field in which one object is the same and one object is different. Significantly more time spent sniffing the novel object than the familiar object represents the definition of novel object recognition.
The subject mouse is placed in an open field containing two identical objects. At a time point such as one hour later, the subject is returned to the open field in which one object is the same and one object is different. Significantly more time spent sniffing the novel object than the familiar object represents the definition of novel object recognition.
Olfactory Habituation/Dishabituation
 The mouse is placed in a clean, empty cage with a cotton swab containing an odor. Ability to detect and discriminate odors is evaluated by time spent sniffing the swab. A series of odors is presented, e.g. water, water, water, almond extract, almond, almond, banana oil, banana, banana, social odor #1 containing odors from one cage of mice, social odor 1, social odor 1, social odor #2 from another cage of mice, social odor 2, social odor 2. Habituation to the same odor, and dishabituation to a new odor, is detected by time spent sniffing each swab.
The mouse is placed in a clean, empty cage with a cotton swab containing an odor. Ability to detect and discriminate odors is evaluated by time spent sniffing the swab. A series of odors is presented, e.g. water, water, water, almond extract, almond, almond, banana oil, banana, banana, social odor #1 containing odors from one cage of mice, social odor 1, social odor 1, social odor #2 from another cage of mice, social odor 2, social odor 2. Habituation to the same odor, and dishabituation to a new odor, is detected by time spent sniffing each swab.
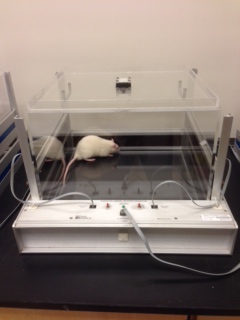
Open Field Exploratory Locomotion
 Photocell beam breaks track locomotor activity as rodents explore a novel open field. Automated equipment provides measures of total distance, horizontal and vertical activity, and center time. Sessions can be a brief 5 minute exposure to a novel open field, or a 1 hour habituation to the open field environment.
Photocell beam breaks track locomotor activity as rodents explore a novel open field. Automated equipment provides measures of total distance, horizontal and vertical activity, and center time. Sessions can be a brief 5 minute exposure to a novel open field, or a 1 hour habituation to the open field environment.
Prepulse Inhibition Of Acoustic Startle
 Startle to a 110 decibel tone is reduced if a quieter tone is introduced 100 msec earlier. Identical hardware equipment is used for acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle, with different software programs.
Startle to a 110 decibel tone is reduced if a quieter tone is introduced 100 msec earlier. Identical hardware equipment is used for acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle, with different software programs.
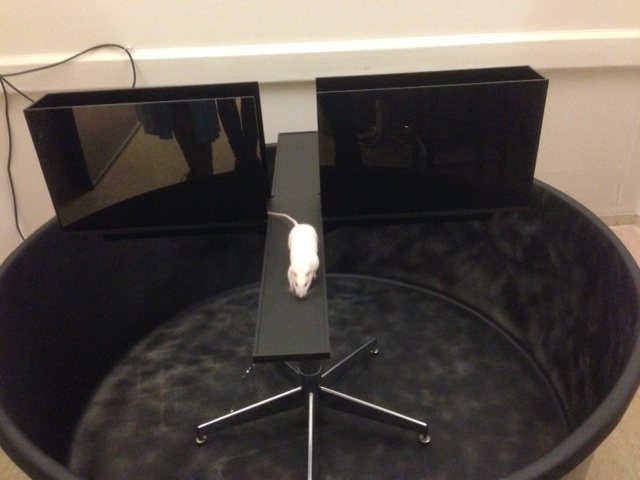
Repetitive Behaviors
 Extended periods of normal behavior patterns such as self-grooming or digging in the litter are scored in mice placed in a clean empty cage. Repetitive behaviors are quantified from videotapes as total time spent engaged in the behavior, and number of bouts.
Extended periods of normal behavior patterns such as self-grooming or digging in the litter are scored in mice placed in a clean empty cage. Repetitive behaviors are quantified from videotapes as total time spent engaged in the behavior, and number of bouts.
Rotarod
 The mouse is placed on the slowly rotating black grooved rubber rod. The rod accelerates from 4 revolutions per minute to 40 revolutions per minute during the 5 minute test session. Latency to fall is the measure of motor coordination and balance.
The mouse is placed on the slowly rotating black grooved rubber rod. The rod accelerates from 4 revolutions per minute to 40 revolutions per minute during the 5 minute test session. Latency to fall is the measure of motor coordination and balance.
Social Approach In 3-chambered Apparatus
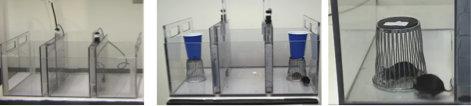 The subject mouse first explores the empty arena. A novel object, the inverted wire pencil cup is placed in one side chamber. A novel mouse inside another wire cup is placed in the other side chamber. More time in the side chamber with the novel mouse than in the side chamber with the novel object defines sociability. Nose-to-nose sniffing is scored from videos of the 10 minute test session, using Noldus Observer event recording software. More time spent sniffing the novel mouse than time spent sniffing the novel object provides a sensitive corroboration of sociability.
The subject mouse first explores the empty arena. A novel object, the inverted wire pencil cup is placed in one side chamber. A novel mouse inside another wire cup is placed in the other side chamber. More time in the side chamber with the novel mouse than in the side chamber with the novel object defines sociability. Nose-to-nose sniffing is scored from videos of the 10 minute test session, using Noldus Observer event recording software. More time spent sniffing the novel mouse than time spent sniffing the novel object provides a sensitive corroboration of sociability.
Social Interactions Between Two Freely Moving Mice
 Specific parameters of reciprocal social interactions between two freely moving mice in the Noldus Phenotyper 3000 arena are scored from videos using Noldus Observer event recording software. Parameters include nose-to-nose sniff, nose-to-anogenital sniff, follow, grooming each other, and climbing over and under each other.
Specific parameters of reciprocal social interactions between two freely moving mice in the Noldus Phenotyper 3000 arena are scored from videos using Noldus Observer event recording software. Parameters include nose-to-nose sniff, nose-to-anogenital sniff, follow, grooming each other, and climbing over and under each other.
Tail Flick
 Latency to move the tail away from the path of an infrared beam measures response to a thermal nociceptive stimulus. A 30 second cut-off avoids tissue damage. Tail flick is considered a spinal reflex.
Latency to move the tail away from the path of an infrared beam measures response to a thermal nociceptive stimulus. A 30 second cut-off avoids tissue damage. Tail flick is considered a spinal reflex.
Tail Suspension
 Time spent immobile is automatically measured in mice suspended by the tail for 5 minutes. Antidepressant treatments reduced immobility time.
Time spent immobile is automatically measured in mice suspended by the tail for 5 minutes. Antidepressant treatments reduced immobility time.
T-Maze
 Food or water reinforcement is located at the end of the right or left long arm of the T-shaped maze. Acquisition of place learning, alternation, delayed non-match to sample, and other learning and memory tasks are conducted. Habituation, shaping, training and testing require several weeks of continuous daily sessions.
Food or water reinforcement is located at the end of the right or left long arm of the T-shaped maze. Acquisition of place learning, alternation, delayed non-match to sample, and other learning and memory tasks are conducted. Habituation, shaping, training and testing require several weeks of continuous daily sessions.
Touch Screen (By Special Request Only)
 Campden/Lafayette touchscreen operant chambers test learning and memory of visual discriminations, reversal learning, delayed non-matching to position, 5-choice serial reaction time, and other complex tasks. The reinforcer is a liquid diet, for food-restricted subject mice. Habituation, shaping, training and testing require several weeks of continuous daily sessions.
Campden/Lafayette touchscreen operant chambers test learning and memory of visual discriminations, reversal learning, delayed non-matching to position, 5-choice serial reaction time, and other complex tasks. The reinforcer is a liquid diet, for food-restricted subject mice. Habituation, shaping, training and testing require several weeks of continuous daily sessions.
Ultrasonic Vocalizations (By Special Request Only)
 Mice emit calls in the ultrasonic range, e.g. by pups separated from the mother and nest, and by adult males during male-female reciprocal social interactions. Ultrasonic vocalizations are detected by a sensitive Avisoft ultrasonic microphone. Recorded vocalizations are analyzed by the Avisoft software for parameters including number of calls, pitch and loudness. Videorecording of social behaviors and audiorecording of the vocalizations are conducted simultaneously.
Mice emit calls in the ultrasonic range, e.g. by pups separated from the mother and nest, and by adult males during male-female reciprocal social interactions. Ultrasonic vocalizations are detected by a sensitive Avisoft ultrasonic microphone. Recorded vocalizations are analyzed by the Avisoft software for parameters including number of calls, pitch and loudness. Videorecording of social behaviors and audiorecording of the vocalizations are conducted simultaneously.
Wire Hang
 The mouse is placed on a wire cage lid. Masking tape at the edges prevents the mouse from walking off the edges. The lid is inverted over a cage containing soft litter. Time to fall is measured with a stopwatch. Most mice can grip the wire throughout the 60 second test session, indicating normal muscle strength.
The mouse is placed on a wire cage lid. Masking tape at the edges prevents the mouse from walking off the edges. The lid is inverted over a cage containing soft litter. Time to fall is measured with a stopwatch. Most mice can grip the wire throughout the 60 second test session, indicating normal muscle strength.
Acoustic Startle
 Sensory function is measured by auditory thresholds, sensory gating (prepulse inhibition; PPI), CNS responsiveness (startle amplitude), and adaptability (startle habituation). This test utilizes an automated system (San Diego Instruments, San Diego, California).
Sensory function is measured by auditory thresholds, sensory gating (prepulse inhibition; PPI), CNS responsiveness (startle amplitude), and adaptability (startle habituation). This test utilizes an automated system (San Diego Instruments, San Diego, California).
Barnes Maze
 The Barnes maze is a “dry-land” version of the Morris water maze in which rats are required to find a darkened escape hole when placed on a well-lighted platform with 18 possible escape locations. This task is used to assess spatial learning and memory along with, or in place of, Morris water maze learning. Normal learning requires 1-2 daily sessions.
The Barnes maze is a “dry-land” version of the Morris water maze in which rats are required to find a darkened escape hole when placed on a well-lighted platform with 18 possible escape locations. This task is used to assess spatial learning and memory along with, or in place of, Morris water maze learning. Normal learning requires 1-2 daily sessions.
Developmental milestones
General health of the animals is assessed after arrival at the testing facility. Neonatal rats are examined for markers of normal development, including sensory and motor function (e.g., paw placing, cliff aversion, wire hang), eye opening, tooth eruption and fur development. These tests are based on the Wahlsten neurodevelopmental test battery.
Drug treatments (by special request only)
Acute and chronic administration of compounds, using intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, oral, and intranasal routes of administration, can be conducted by investigators in the dedicated procedure room, or can be conducted by Core staff upon request.
EEG

Electroencephalograpy using telemetry to detect seizures, sleep architecture, and power spectral analyses. Spiking events and powerband calculations are collected via wireless telemetry and automatically scored using Neuroscore. Custom algorithms tailored to investigator questions are also offered upon request, such as active-wake-sleep cycles and circadian rhythms.
Elevated plus-maze
 Rats are placed for 5 min in the center of a four-arm "Plus" maze elevated 2 feet above the floor. Two of the arms have side walls, while two are open at the sides. More fearful rats spend a greater percentage of time in the center of the arms with side walls, than on the open arms.
Rats are placed for 5 min in the center of a four-arm "Plus" maze elevated 2 feet above the floor. Two of the arms have side walls, while two are open at the sides. More fearful rats spend a greater percentage of time in the center of the arms with side walls, than on the open arms.
Fear conditioning
 Contextual and cued fear conditioned learning and memory are quantified by freezing behavior in automated Med Associates fear conditioning chambers.
Contextual and cued fear conditioned learning and memory are quantified by freezing behavior in automated Med Associates fear conditioning chambers.
Metabolic Monitoring
 Comprehensive Laboratory Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS): The CLAMS instrument (Columbus Instruments) will be used to assess multiple variables that influence net calorie balance and the utilization of carbohydrate, fat, or protein for energy in mutant rat models. It is a temperature controlled rodent activity, feeding and indirect calorimeter system fully-integrated animal behavioral and metabolic monitoring system, designed to support multiple-user applications for studies involving rats. Running wheels and treadmills are also available for use with this system.
Comprehensive Laboratory Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS): The CLAMS instrument (Columbus Instruments) will be used to assess multiple variables that influence net calorie balance and the utilization of carbohydrate, fat, or protein for energy in mutant rat models. It is a temperature controlled rodent activity, feeding and indirect calorimeter system fully-integrated animal behavioral and metabolic monitoring system, designed to support multiple-user applications for studies involving rats. Running wheels and treadmills are also available for use with this system.
Morris Water Maze
 In this spatial learning and memory task, rats are typically given 4 daily trials over 5 days of training. Training and testing sessions include visible platform trials, probe trials, as well as reversal learning and tests of relearning. The rat is placed in a pool of water and required to find a hidden escape platform below the water surface. Environmental spatial cues are available to assist them in finding the platform. The Morris water maze is widely used to assess the cognitive ability of rats. A variety of test protocols assess learning, working, short term and long term memory, selective attention, discrimination and generalization. Animal performance in this test, including swim distance, swim speed, latency find the hidden platform, is recorded and analyzed using a computer-based tracking system (Noldus Ethovision).
In this spatial learning and memory task, rats are typically given 4 daily trials over 5 days of training. Training and testing sessions include visible platform trials, probe trials, as well as reversal learning and tests of relearning. The rat is placed in a pool of water and required to find a hidden escape platform below the water surface. Environmental spatial cues are available to assist them in finding the platform. The Morris water maze is widely used to assess the cognitive ability of rats. A variety of test protocols assess learning, working, short term and long term memory, selective attention, discrimination and generalization. Animal performance in this test, including swim distance, swim speed, latency find the hidden platform, is recorded and analyzed using a computer-based tracking system (Noldus Ethovision).
Novel Object Recognition

Recognition of a novel object as compared to a familiar object is quantified with Noldus Ethovision multiple body points module.
Open Field Exploratory Locomotion
The open field apparatus (Accuscan Instruments, Columbus, OH) measures locomotor activity (horizontal and vertical). The animal is placed in an isolated chamber (16.5 inch square) for 30-60 minutes. Locomotor activity is recorded using beam break technology. Measures include rearing, horizontal activity, stereotypy movements, and zone duration and distance. Activity patterns, including peak and average activity in a novel or familiar environment, as well as rest-activity cycles are recorded.
Prosocial motivational escape
Prosocial motivational escape is a test of social motivation. The subject rat learns to open a door to a Plexiglas chamber, allowing a trapped rat to escape.
Rotarod
Rotarod performance assesses motor coordination and balance. This test has previously been shown to be sensitive to cerebellar irradiation damage in rats. Animals are placed on a moving cylinder and required to walk with the designated speed. Time and speed is recorded when the animal falls off the cylinder. Testing requires one training sessions and 3 test session over a 3 day period.
Social Approach In 3-chambered Apparatus

The subject rat first acclimates to the enclosure for 10 minutes. A novel rat is then placed in one of the side zone cage and the test animal is again released in the center compartment and videotaped for ten minutes to become familiarized with the object rat. Lastly, an additional object rat (novel) is placed in the empty cage and the test rat again is filmed for ten minutes to record its behavior. The test utilizes a tracking system (Ethovision) to record time spent in each zone and sniffing around the rats in the cages.
Social Interactions Between Two Freely Moving Rats
Rats are videotaped over a 30 min social encounter. This is a non-invasive observational study of social interactions between conspecifics. Examples of behaviors to be scored are grooming, digging, exploring, crawling over, inactivity, stereotypy, following, sniffing, freezing, aggression bouts, and rearing.
T-Maze
 The T-maze is used to assess spatial learning, response learning, or to quantify spontaneous alternation activity. The rat is placed in the start arm of a “T” shaped Plexiglas maze and allowed to spontaneously alternate between arms, or are trained to find a reward (e.g., food, water) by using a response strategy (e.g., turn right), or by using spatial cues available in the room. Animal performance is recorded and analyzed using Noldus Ethovision software and tracking equipment.
The T-maze is used to assess spatial learning, response learning, or to quantify spontaneous alternation activity. The rat is placed in the start arm of a “T” shaped Plexiglas maze and allowed to spontaneously alternate between arms, or are trained to find a reward (e.g., food, water) by using a response strategy (e.g., turn right), or by using spatial cues available in the room. Animal performance is recorded and analyzed using Noldus Ethovision software and tracking equipment.
Ultrasonic Vocalizations (By Special Request Only)
 Neonatal rat pups emit ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs) when isolated from their mothers. USVs following maternal separation are used as an index of fearfulness and distress in pups. Ultrasonic vocalization recordings are conducted on postnatal days up to age 18 days. Emissions of USVs from the pups are directly sensed by the Ultravox microphone located at the top of the chamber and the signal information (e.g. the frequency and duration of USVs) are transmitted to the UltraVox (Noldus) software program.
Neonatal rat pups emit ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs) when isolated from their mothers. USVs following maternal separation are used as an index of fearfulness and distress in pups. Ultrasonic vocalization recordings are conducted on postnatal days up to age 18 days. Emissions of USVs from the pups are directly sensed by the Ultravox microphone located at the top of the chamber and the signal information (e.g. the frequency and duration of USVs) are transmitted to the UltraVox (Noldus) software program.
Additional behavioral assays for mice and rats are available on request, and/or can be modified and developed, to meet specific requests by Core Users.
Animal Housing And Transfers:
Mouse Vivarium: The UC Davis mouse vivarium in the Research II building in Sacramento is secure facility. Controls are automated for lighting and temperature. Veterinary care and husbandry is provided by the University of California Davis animal care program (Campus Veterinary Services, TRACS). Mice are housed in Tecniplast filter top cages within an air filtration rack system in the vivarium. Sentinels are used to ensure the health of the animals. Transfer of animals must be approved by the Campus Veterinary Office using the online Animal Transfer System request form. Arrival dates are limited to Wednesdays and Thursdays. The request form must state that the transfer staff must give 48 hours notice to the Research II vivarium staff, to provide time to prepare the new cages for the expected arrival day. After arrival and before behavioral testing, mice are typically acclimated to the vivarium for one week. Entry into the vivarum is limited to animal care personnel and investigators with specified training and approval. Personal protective equipment (PPE), including dedicated lab coats and gloves, are worn while working with the animals. Rooms and equipment are maintained in sanitary condition at all times.
Rat Vivarium: The UC Davis rat vivarium in Tupper Hall is an environmentally controlled (lighting, temperature, humidity) facility, with veterinary care and husbandry provided by the UC Davis animal care program (TRACS). Rats are housed in filter top cages and under an air filtration rack system while in the vivarium. Sentinels are used to ensure the health of the animals. Transfer of animals must be approved by the Campus Veterinary Office and the Core manager. The facility has the capacity to house up to 250 rats. Before behavioral testing rats are typically acclimated to the vivarium for one week. Entry is limited to animal care personnel, staff, investigators and students that have been trained to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) while working with the animals, and safety trained and documented. Rooms and equipment are maintained in sanitary condition at all times.
01. Database front page, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
02. Acoustic startle graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
03. Acoustic startle spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
04. Elevated plus-maze graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
05. Elevated plus-maze spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
06. Juvenile reciprocal social interaction graphs,UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
07. Juvenile reciprocal social interactions spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
08. Light-dark transitions graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
09. Light-dark spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
10. Male-female social interaction and vocalization graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
11. Male-female social interaction and vocalization spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
12. Marble burying graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
13. Marble burying spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
14. Novel object recognition graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
15. Novel object recognition spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
16. Open field graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
17. Open field spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
18. Prepulse inhibition graph, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
19. Prepulse inhibition spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
20. Rotarod graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
21. Rotarod spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
22. Self-grooming graphs, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
23. Self-grooming spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
24. Three-chambered social approach graphs.pdf
25. Three-chambered social approach spreadsheet, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.xlsx
26. Sources of original data, UC Davis MIND Institute IDDRC, 2020.pdf
Projects with high relevance to intellectual and developmental disabilities may be eligible for a discounted rate for consultation and behavioral testing services. Requests for approval are submitted to Director Leonard Abbeduto and the Executive Committee of the Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center (IDDRC), which is funded by an NICHD grant to the MIND Institute at UC Davis.
If you are not an IDDRC approved project, please submit a request for approval.
IDDRC - Research Project Application Form
For questions, please contact Michele Ono, Project Manager myono@ucdavis.edu
Submit a request for IDDRC Rodent Behavior Core
For Questions, please contact:
Jill Silverman, Ph.D., Mouse Core Co-Director, jsilverman@ucdavis.edu
Melissa Bauman, Ph.D., Rat Core Co-Director, mdbauman@ucdavis.edu