Eczema
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
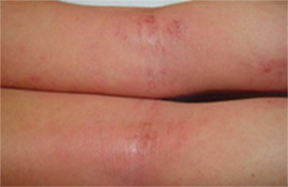 Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that can appear in infancy, childhood or adulthood. It often causes inflamed, itchy skin, and with long-term disease, the skin can become thickened, scaly, cracked or prone to infection.
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that can appear in infancy, childhood or adulthood. It often causes inflamed, itchy skin, and with long-term disease, the skin can become thickened, scaly, cracked or prone to infection.
The condition tends to come and go, with periods of remission and flare-ups. It often runs in families and may be associated with asthma or seasonal allergies. Symptoms can worsen in the winter, and stress may also trigger flares.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure, effective management focuses on protecting and moisturizing the skin. Patients are encouraged to use fragrance-free soaps, emollients and detergents. Moisturizing regularly is the single most important step in controlling symptoms.
Medical treatments may include topical steroids or immunomodulators, such as Elidel or Protopic, which reduce inflammation with fewer side effects than traditional steroids. Antihistamines can help control itching and prevent the itch-scratch cycle. For more severe cases, additional options such as light therapy, oral steroids or systemic immunosuppressants may be recommended.
Educational Videos
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule an appointment, please call 916-734-6111 or 800-770-9282.