Skin Cancer
Your Partner in Skin Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
 It is understandable to have concerns if you receive a skin cancer diagnosis. The good news is that skin cancer typically responds well to treatment, especially when identified early.
It is understandable to have concerns if you receive a skin cancer diagnosis. The good news is that skin cancer typically responds well to treatment, especially when identified early.
At UC Davis Health, we expertly diagnose and treat common, rare and aggressive forms of skin cancer. We combine advanced technology, leading-edge treatments and compassionate care to ensure you receive the best possible outcome.
See skin cancer treatments »
Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops when abnormal, cancerous skin cells start to rapidly grow and replace healthy cells. Over time, these cancerous cells can invade surrounding tissue and, in some cases, spread to other parts of the body. Skin cancer can affect people of all ages, genders and ethnicities, making regular skin checks and sun protection important for everyone. It is also the most common form of cancer in the United States, with millions of new cases diagnosed each year.
Among the different types of skin cancer, melanoma is the most serious and potentially life-threatening. It develops in the pigment-producing cells that give skin its color. If detected early, melanoma can often be treated successfully, but if left untreated, it can spread quickly to other organs. Due to its aggressive nature, prompt recognition and treatment are critical.
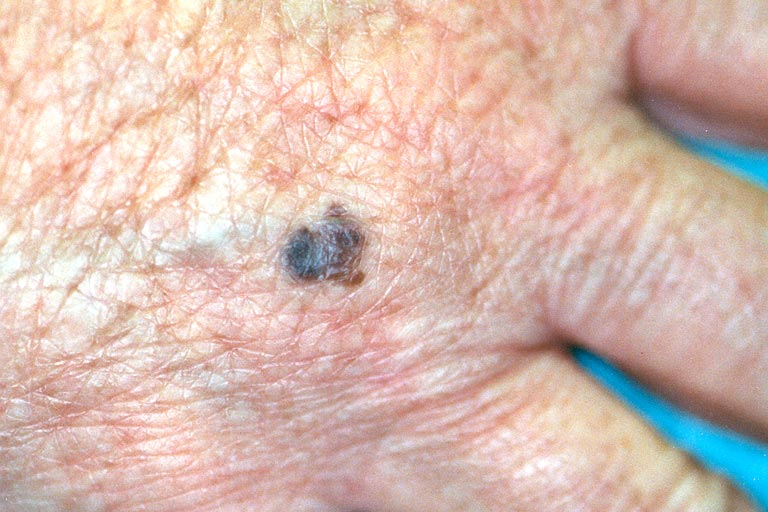
What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Signs of skin cancer vary depending on cancer type, location, skin tone and other factors.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
- A mole that looks different from other moles
- Asymmetrical moles (one side is a different shape than the other side)
- Changes to existing moles
- Multicolored moles
- Reddish, scaly growths
- Sores that do not heal
- Thickened wart-like growths
Where Skin Cancer Appears
Skin cancer most commonly appears on sun-exposed areas, but it may develop anywhere.
Skin cancer can affect the:
- Face
- Chest
- Legs and feet
- Shoulders, arms and hands
- Underneath fingernails and toenails
- Genitals
- Inside the mouth
Skin Cancer Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds is the leading cause of skin cancer. UV rays damage the DNA in skin cells, and over time, this damage can build up, leading to abnormal cell growth and the development of cancer. Even short periods of unprotected sun exposure can have lasting effects, making sun protection and regular skin checks essential for prevention.
Other risk factors include:
- Age (people over age 50 are more at risk due to years of sun exposure)
- Blonde or red hair
- Fair skin
- Family history of melanoma
- History of sunburns, especially blistering burns
- Moles (people with 50 or more moles have a higher risk)
- Weakened immune system
Types of Skin Cancer
We treat all forms of skin cancer, including:
- Basal cell carcinoma — This slow-growing cancer is the most common skin cancer. It responds well to treatments when caught early and small.
- Squamous cell carcinoma — This skin cancer can spread and grow deep into the skin, especially when care is delayed.
- Melanoma — Melanoma is a cancer of pigment-producing cells in the skin. It can quickly spread to organs or other parts of the body if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are key.
- Merkel cell carcinoma — This rare type of skin cancer is aggressive and can spread quickly even with treatment.
- Skin adnexal tumor — These potentially cancerous tumors develop in hair follicles, sweat glands and oil glands.
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) — Mutated white blood cells called T-lymphocytes attack the skin and can also be present in blood, organs and lymph nodes.
- Kaposi sarcoma — This cancer most frequently affects people living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Choosing UC Davis Health for Skin Cancer Care
Whether you have a more common type of skin cancer or a cancer that’s large and complex, we have the expertise to help. At UC Davis Health, you have access to:
Mohs Micrographic Surgery Experts
Our team specializes in Mohs micrographic surgery, the most effective treatment for basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. This precise procedure removes the cancer and cures it in a single appointment. Our fellowship-trained skin cancer specialists, Daniel Eisen, M.D., and Jayne Joo, M.D., also perform Mohs surgery for melanoma — a procedure that requires advanced training and extensive experience.
Latest Therapies
By actively participating in dermatology research and clinical trials, your care team is committed to advancing skin cancer treatments and improving outcomes. We also strive to refine surgical techniques to reduce pain and scarring. Our dedication to research ensures you have access to promising new therapies.
Comprehensive, Hospital-Quality Care
Skin cancer biopsies and surgical treatments begin with an injection of a local anesthetic to numb the area. Complex tumors can sometimes require more invasive surgery. These outpatient procedures are extremely safe. You have the extra assurance of receiving care at UC Davis Medical Center. U.S. News & World Report rates our medical center as the best in Sacramento and among the top 10 in the state.
Personal Touch
Your physician and our qualified staff will share biopsy results with you directly and answer any questions about your diagnosis or treatment. Our goal is to ensure you feel informed, comfortable, and confident in your care plan.
Scar-Minimizing Procedures
We are dedicated to eliminating skin cancer while minimizing scarring. Some skin cancers can affect large sections of skin or go deep into the skin. We perform reconstructive procedures that result in the best appearance possible.
See more about our skin cancer treatments »
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule an appointment, please call 916-734-6111 or 800-770-9282.